Qt is supported on a variety of 32-bit and 64-bit platforms, and can usually be built on each platform with GCC, a vendor-supplied compiler, or a third party compiler. In Qt Creator, a kit specifies the compiler and other necessary tools for building an application for and running it on a particular platform.
Qt Creator automatically detects the compilers that are registered by your system or by the Qt Installer and lists them in 工具 > Options > Kits > 编译器 :
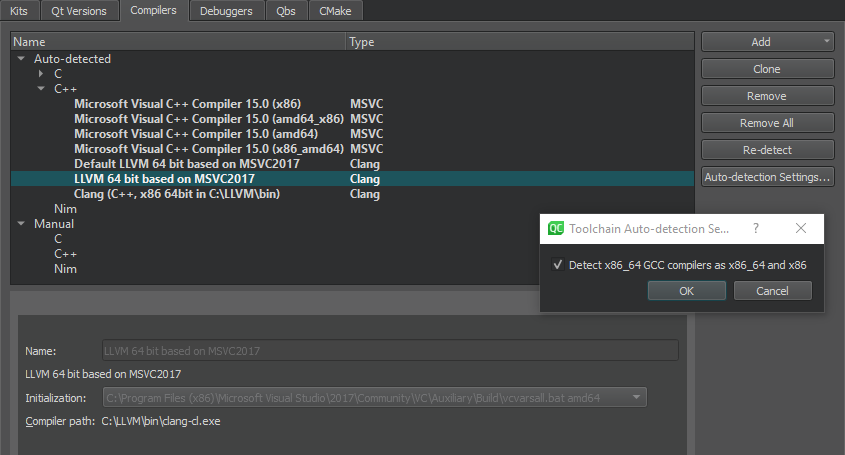
You can add the following compilers to build applications by using other compilers or by using additional versions of the automatically detected compilers:
cl.exe
.
In addition, the Qt Creator Bare Metal Device plugin provides support for the following compilers:
注意:
Currently supported architectures are
8051
,
AVR
,
ARM
,
STM8
,和
MSP430
.
注意:
Currently supported architectures are
8051
and
ARM
.
注意:
Currently supported architectures are
8051
and
STM8
.
When Qt Creator finds an x86_64 GCC compiler, it sets up an instance for the native x86_64 target. If you plan to create also 32-bit x86 binaries without using a dedicated cross-compiler, select Auto-detection Settings > Detect x86_64 GCC compilers as x86_64 and x86 . Then select Re-detect to refresh the list of automatically detected compilers.
To remove manually added compilers, select 移除 or Remove All .
To build an application using GCC, MinGW, Clang, or QCC, specify the path to the directory where the compiler is located and select the application binary interface (ABI) version from the list of available versions. You can also create a custom ABI definition. For QCC, also specify the path to the QNX Software Development Platform (SDP).
To enable Microsoft Visual C++ Compilers (MSVC) and clang-cl to find system headers, libraries, and the linker, Qt Creator executes them inside a command prompt where the environment has been set up using
vcvarsall.bat
. For these compilers, you also specify the path to the script that sets up the command prompt.
You specify the compiler to use for each kit in 工具 > Options > Kits .
To add C or C++ compilers:
To clone the selected compiler, select Clone .
The other settings to specify depend on the compiler.
To build an application using the Nim Compiler, select 工具 > Options > Kits > 编译器 > Add > Nim , and specify the path to the directory where the compiler is located.
To add a compiler that is not listed above or a remote compiler, use the 自定义 option and specify the paths to the directories where the compiler and make tool are located and options for the compiler.
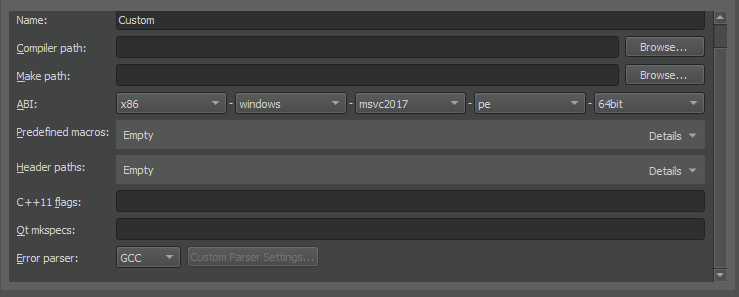
To add other compilers:
If error messages displayed in the
Compile Output
pane contain paths where slashes are missing (for example,
C:QtSDK
), check your PATH variable. At the command line, enter the following commands:
where sh.exe where make.exe where mingw32-make.exe
If these commands show paths, they have been added to the global PATH variable during the installation of a tool chain based on Cygwin or MinGW, even though this is against Windows conventions.
To keep working with the third-party tool chain, create a new shell link that adds the required paths (as Visual Studio and Qt do). The shell link must point to cmd.exe, as illustrated by the following example:
C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /K C:\path_to\myenv.bat
where the /K parameter carries out the command specified in the bat file.
Create the myenv.bat file at path_to , which should be in a convenient location. In the file, specify the paths to the tool chains. For example,
set PATH=C:\path1;C:\path2;%PATH%
where path1 and path2 are paths to the tool chains.
Finally, remove the paths from the global PATH, reboot the computer, and run the
where
commands again to verify that the global PATH is now clean.
You can use the shell link to run the tools in the third-party tool chains.