Different build configurations allow you to quickly switch between different build settings. By default, Qt Creator creates debug , release ,和 profile build configurations. A debug build contains additional debug symbols that you need for debugging the application but that you can leave out from the release version. Generally, you use the debug configuration for testing and the release configuration for creating the final installation file.
If you selected CMake as the build system for the project, you can use a minimum size release build configuration to create the final installation file. It is a release build that makes the size of the binary package as small as possible, even if this makes the application slower.
A profile build (which is called release with debug information when using CMake) is an optimized release build that is delivered with separate debug information. It is best suited for analyzing applications.
You specify build settings in the Projects mode. To add a new build configuration, click Add and select the type of configuration you would like to add. The options you have depend on the build system that you selected for the project. You can add as many build configurations as you need. You can also select Clone to add a build configuration that is based on the currently selected one.
选择 Rename to give the currently selected build configuration a new name.
To delete the build configuration currently selected, click 移除 .
Select the build configuration to edit in the Edit build configuration field.
The available build settings depend on the build system that you selected for the project.
Since Qt 5.11, you can compile QML source code into the final binary. This improves the startup time of the application and eliminates the need to deploy QML files together with the application. For more information, see Ahead-of-Time Compilation .
Qt Creator project wizard templates create Qt Quick projects that can be compiled, because they are set up to use the Qt Resource System. To compile Qt Quick code, select Enable 在 Qt Quick 编译器 field. To use default settings, select Leave at Default .
注意: In earlier Qt versions, this was a commercial feature. For more information, see Qt Quick 编译器 .
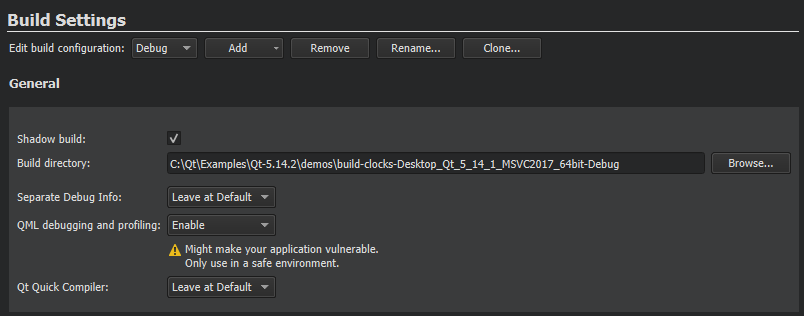
By default, Qt Creator builds projects in a separate directory from the source directory, as shadow builds . This keeps the files generated for each build and run kit separate. If you only build and run with a single kit , you can deselect the Shadow build checkbox.
To make in-source builds the default option for all projects, select 工具 > Options > Build & Run > Default Build Properties , and enter a period (.) in the Default build directory field.
You can create separate versions of project files to keep platform-dependent code separate. You can use qmake scopes to select the file to process depending on which platform qmake is run on.
To generate debug symbols also for applications compiled in release mode, select Enable 在 Separate debug info field. For more information, see Using the Performance Analyzer . To use default settings, select Leave at Default .
To set the default build properties, select 工具 > Options > Build & Run > Default Build Properties .
Configuring medium-sized to large CMake projects in Qt Creator can be a challenge due to the number of options that you need to pass to CMake to configure the project correctly. Qt Creator creates an initial configuration for you based on the kit settings and displays it in the Initial CMake parameters field.
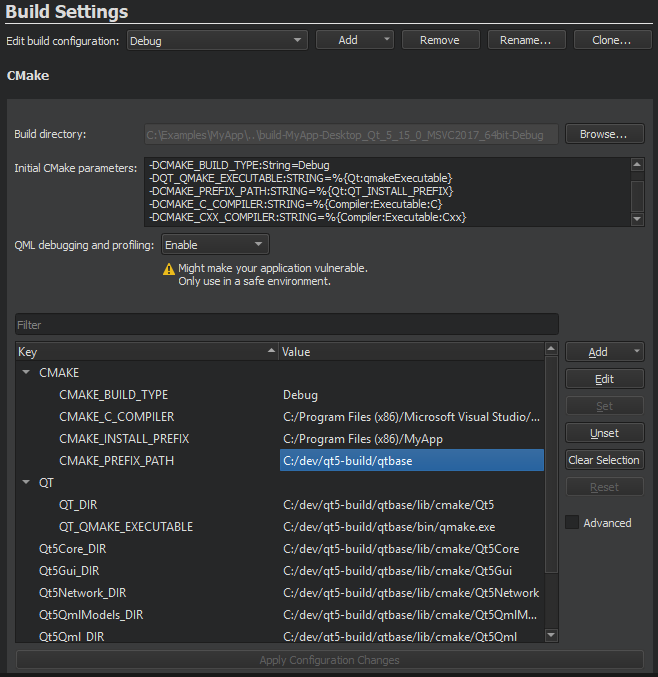
在 Value column, you can view and edit the actual values of the parameters that are passed to CMake. Parameter names are listed in the Key column. Names with a common prefix (up to the first underscore character) are grouped under the prefix. To view all parameters, select the 高级 check box.
To add parameters, select Add , and then select the type of the parameter that you are adding: 布尔 , 字符串 , Directory ,或 File .
To change the type of the selected parameter, right-click the parameter name in the Key column, and then select Force to bool , Force to file , Force to directory ,或 Force to string 在上下文菜单。
To modify the value of a parameter, double-click it, or select it, and then select Edit .
You can apply actions to multiple parameters at a time. To clear the selection, select Clear Selection .
To remove the selected parameters, select Unset . To undo the removal, select Set .
To reset all the changes that you made, select Reset .
To save the changes, select Apply Configuration Changes . Keep in mind that a configuration change might trigger a follow-up configuration change.
The parameter values that you change are passed via
-D<option>=<value>
to CMake, which stores the options in the CMakeCache.txt file. This means that if you remove the build directory, all the custom parameters that are not part of the initial CMake parameters are also removed.
To reconfigure a project after making changes to the initial parameters, select 构建 > Clear CMake Configuration , which removes the CMakeCache.txt file. This enables you to do a full rebuild.
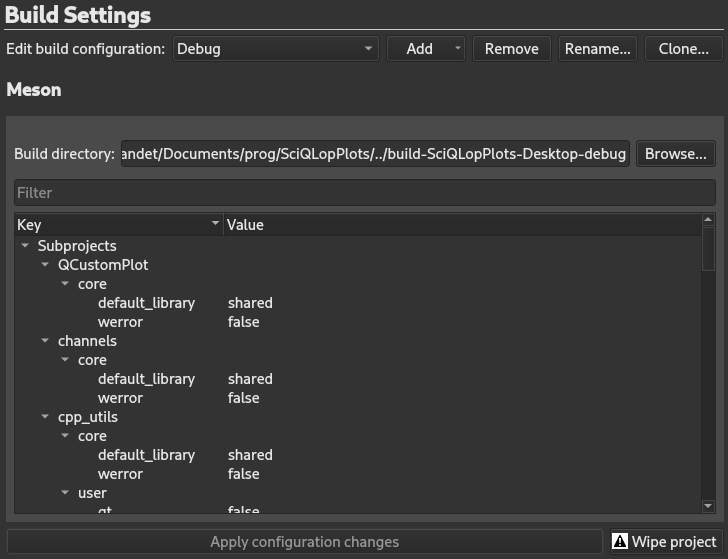
Settings are grouped by category by Meson. All items are user modifiable except
backend
which is forced to Ninja,
buildtype
,
debug
及
optimization
to ensure a good compatibility with Qt Creator.
Each setting type has its own editor. To modif any setting, double-click it, either edit the field, or select your choice depending on the control. To apply changes, select
Apply configuration changes
. This will trigger a
meson configure
command if there were any configuration changes. If for any reason the build directory configuration is broken, select
Wipe project
. This should fix any build directory.
注意: Any modified setting will remain in bold until Apply configuration changes is selected.
Qt Creator executes external processes to accomplish tasks such as building and running applications. To execute the processes, Qt Creator uses shell commands that are native to the system. It constructs the commands from an executable name and optional command line arguments.
The executable name is specified in the executable fields: qmake , Make , Command ,或 Executable . It is either derived from the project or specified manually. When you specify executables manually, you can reference environment variables and Qt Creator variables. However, no quoting rules apply.
You can specify command-line arguments in the arguments fields: 自变量 , Additional arguments , CMake arguments , Command arguments , Default arguments , Extra arguments , Make arguments ,或 Tool arguments . You can create shell command lines that can contain redirection and other advanced constructs. However, some more complex use cases, such as piping test data into the application being tested or grouping commands, are not supported because the value of the Executable field is always placed first when constructing the command.
可以使用 environment variables as values in the fields. In addition, you can use Qt Creator variables in arguments, executable paths, and working directories.
在 Build Steps you can change the settings for the build system selected for building the project: qmake, CMake, Meson, or Qbs. You can use Incredibuild to accelerate the build process when using qmake or CMake.
Qt Creator builds qmake projects by running the
make
or
nmake
command from the Qt version defined for the current build configuration.
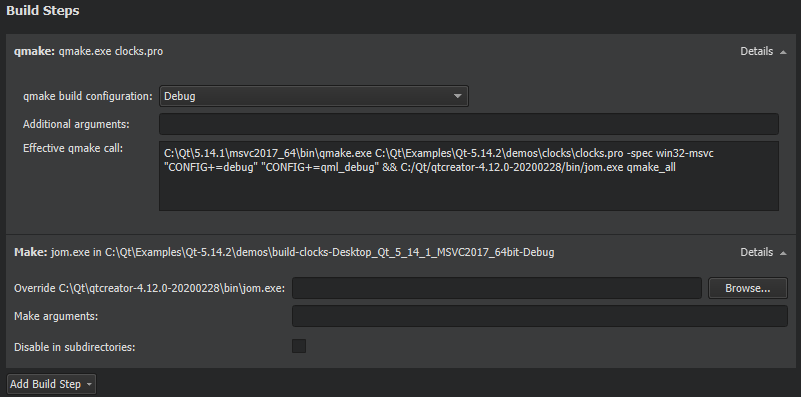
To override the shell command that Qt Creator constructs by default, disable or remove the build step and add a custom build step that specifies another shell command.
By default, Qt Creator uses all the CPU cores available to achieve maximum build parallelization. On Linux and macOS, you can specify the number of parallel jobs to use for building in the Parallel jobs field. Select the Override MAKEFLAGS check box to override existing MAKEFLAGS variables.
Qt Creator builds CMake projects by running
cmake . --build
, which then runs the CMake generator specified in the project configuration:
make
,
mingw32-make
,
nmake
,或
ninja
, for example. The CMake generator produces project files for Qt Creator.
You can add arguments to pass to CMake and the generator and targets for the build command in Build Steps .
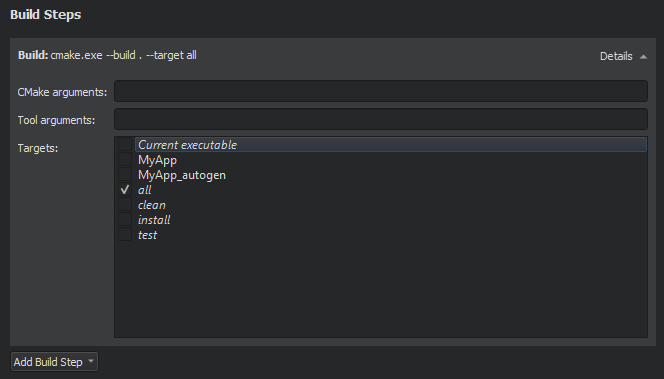
注意: While the other CMake generators are installed together with Qt, you usually need to install Ninja yourself. For more information, see Using Ninja as a CMake Generator .
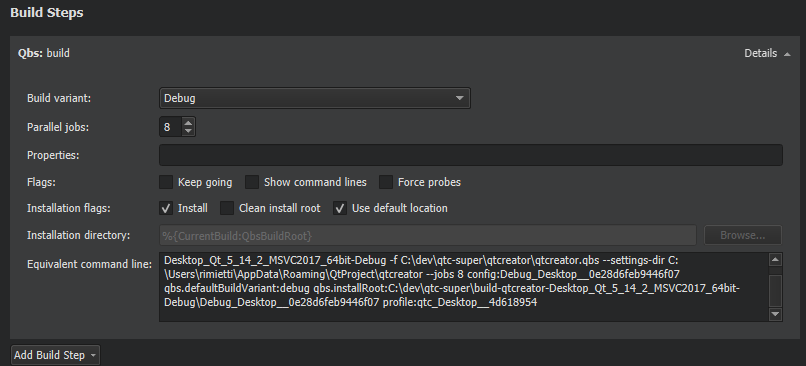
To specify build steps for Qbs:
注意: On Windows, the build will fail if the application is running, because the executable file cannot be overwritten. To avoid this issue, you can deselect this check box and add a Qbs Install deployment step in the run settings that will be performed just before running the application.
The Equivalent command line field displays the build command that is constructed based on the selected options.
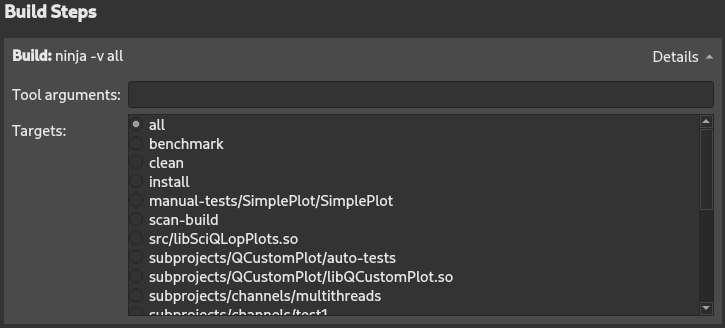
Qt Creator builds Meson projects by running
ninja -v target
.
You can add arguments and targets for the build command in Build Steps .
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in the Issues output pane.
To use IncrediBuild, select Add Build Step > IncrediBuild for Linux or IncrediBuild for Windows .
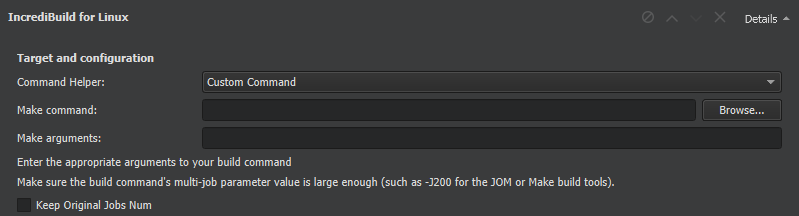
IncrediBuild automatically detects the build step by iterating over the build steps you already defined. The initial build step settings will be part of your IncrediBuild build step, so your usual build tool will still be used, but with the added benefit of IncrediBuild's build acceleration and graphical Build Monitor.
在 Target and configuration group, specify the command helper and arguments that will be used to construct the build command.
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in the Issues output pane.
Select the
Keep original jobs number
check box to stop IncrediBuild from overriding the
-j
command line switch, which controls the number of processes that the build tools executed by Qt Creator run in parallel. The default value set by IncrediBuild is 200.
The distribution control settings to specify depend on whether you are using Linux or Windows.
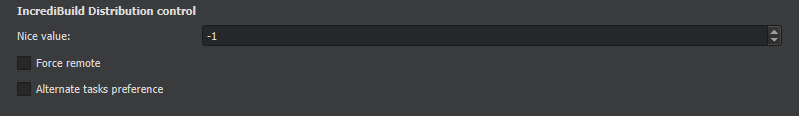
You can specify the following options for Linux builds:
allow_remote
tasks to remote Helpers.
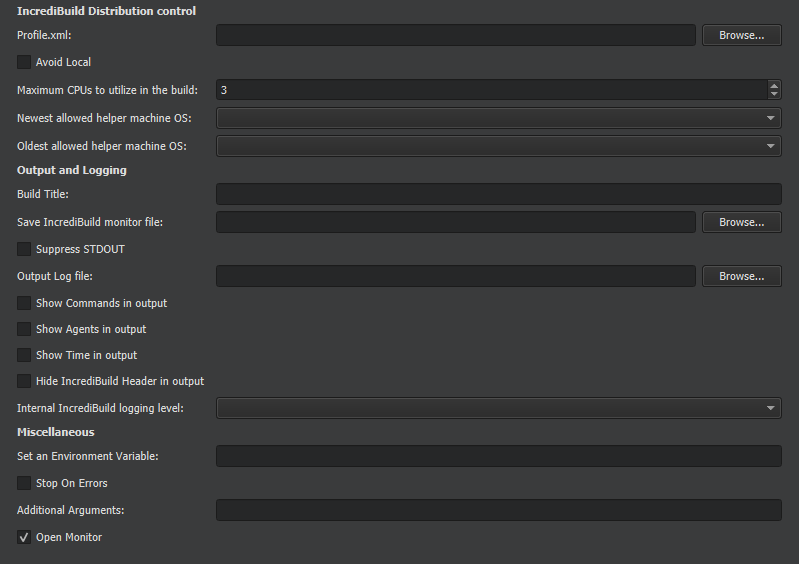
You can specify the following options for Windows builds:
.ib_mon
) file to the specified location. If only a folder name is given, IncrediBuild generates a GUID for the file name. A message containing the location of the saved
.ib_mon
file is added to the end of the build output.
To configure a project to be built using the Conan package manager, select Add Build Step > Run Conan Install .
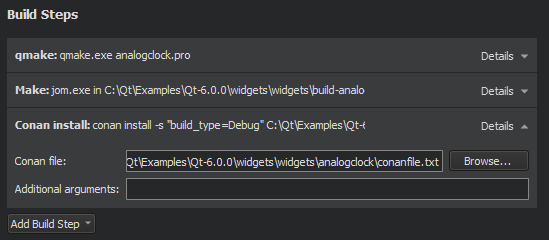
在 Conan file field, enter the location of the conanfile.txt file for the project.
The Conan install field displays the effective build command. You can add arguments for the command in the Additional arguments field.
For more information about configuring Conan, see Setting Up Conan .
To add custom steps to the build settings, select Add Build Step > Custom Process Step .
By default, custom steps are enabled. To disable a custom step, select the
 (
Disable
) button.
(
Disable
) button.
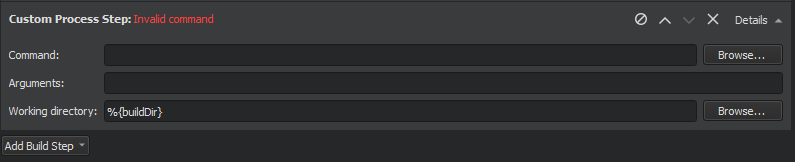
To execute custom commands when building for embedded devices, select Add Build Step > Custom Remote Command (via adb shell) (commercial only) and enter the command to execute.
You can use the cleaning process to remove intermediate files. This process might help you to fix obscure issues during the process of building a project.
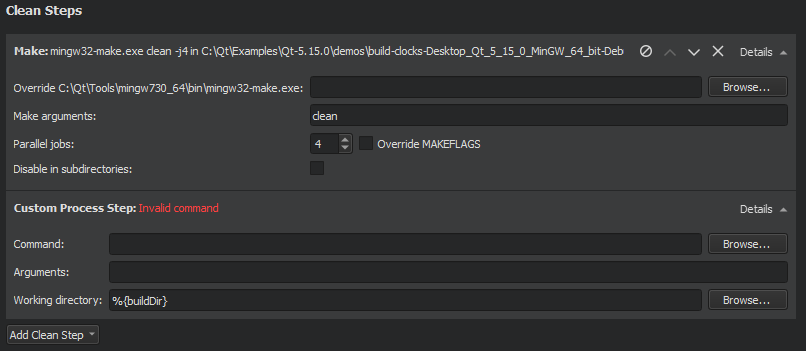
You can define the cleaning steps for your builds in the Clean Steps .
By default, custom steps are enabled. To disable a custom step, select the Disable button.
 (
Move Up
) and
(
Move Up
) and
 (
Move Down
).
(
Move Down
).
When building with CMake, you can add arguments to pass to CMake and the generator and targets for the clean command in Clean Steps .
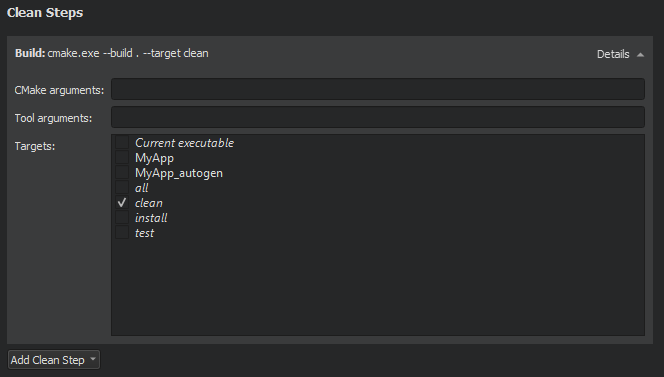
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in the Issues output pane.
When building with Qbs, you can specify flags in Clean Steps :
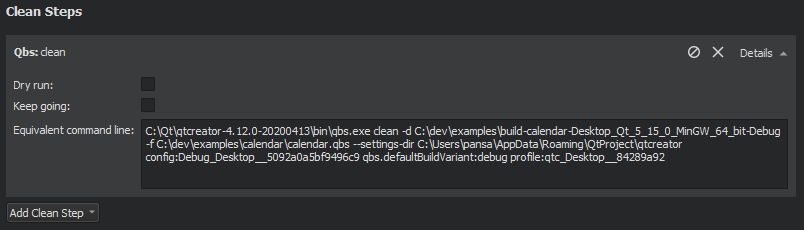
The Equivalent command line field displays the clean command that is constructed based on the selected options.
When building with Meson, you can add arguments and targets for the clean command in Clean Steps .
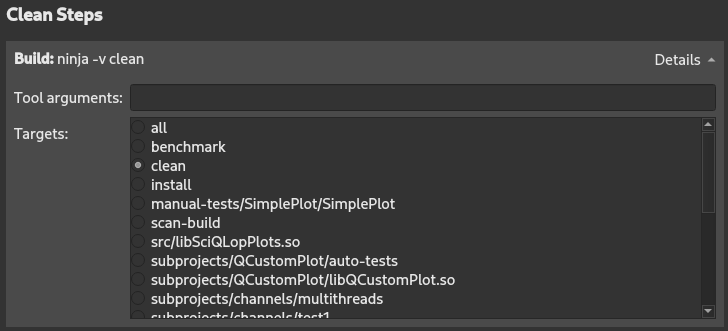
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in the Issues output pane.
When building with IncrediBuild, you can add arguments and targets for the clean command in Clean Steps .
For more information about the settings, see IncrediBuild Build Steps .
The build errors and warnings are parsed and displayed in the Issues output pane.